Optical Network Services in Future Broadband Networks
Introduction
An optical network is a network where the user-network
interface is optical and the data does not undergo
optical-to-electrical conversion within the network as it is
routed to its destinations. Here, we discuss
• Different optical network architectures according to the
services they provide,
• The technologies used to implement those services,
• The geographical size of the network.
There is a great interest in optical network applications in
the wide and metropolitan areas. The reasons are that fiber
optic transmission technology is progressing faster than
electronic switching technology and because optical switching
technology is maturing to the point where it may be the
economic choice in certain situations. Optical transmission
systems supporting 40 Gb/s are commercially available, 100 Gb/s
products have been announced, and terabit-per-second systems
have been demonstrated in the laboratory. All these are
single-fiber systems, while fiber links in metropolitan area
networks (MANs) and wide area networks (WANs) are typically
composed of fiber bundles with tens of fibers per bundle.
Optical networks offer the potential to economically tap this
large capacity.
Theoretically, optical networks could provide almost any
service offered by an electronic network:
• Circuit services,
• Virtual circuit services,
• Datagram services.
However, due to limited technology in optical logic,
buffering, and gating, the most practical technology at this
time allows only high-bandwidth circuit services. This
technology, known as wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)
with wavelength routing, or so called OTN, is a major focus of
this chapter; however, other network services are possible and
nearing practicality.
There are many potential roles that an optical network in a
broad-band architecture can play. An underlying principle in
thinking about these roles is that in most situations, there
is a large mismatch between the services which can practically
be offered by optical networks and those desired by end users.
Therefore, in almost all situations electronic networks must
be overlaid on top of the optical network.
Although optics and electronics can provide similar services,
there are major differences between what can practically be
offered by each technology. For instance, both SDH and WDM can
provide circuits; however, SDH more easily allows the
insertion and removal of data within the circuit than WDM.
There are therefore significant trade-offs between which
services are offered at the optical layer and which by
electronics. The resolution of those trade-offs depend heavily
on the geographical extent of the network because of different
physical layer, topology, and protocol issues as well as
different traffic requirements.
The organization of this chapter is as follows. We first
discuss broadband network architectures and where optics might
play a role in the protocol stack. We then discuss the
services optical networks can deliver, the technologies used
to implement those services, and some of the major
technological limitations. Finally, we use this knowledge base
to analyze the potential role of optics in WANs, MANs, and
then local area networks (LANs).
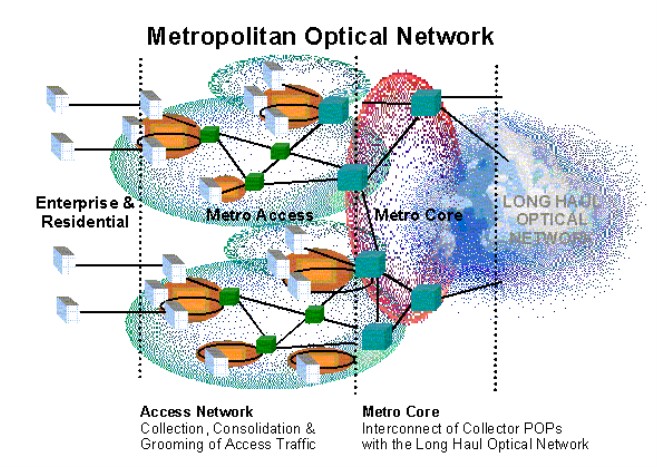
Optical Transport Networks & Technologies Standardization Work
Plan-ITU
ITU standards enhance capabilities of the Optical Transport
Network - ITU Hub
Optical Transport Networks (itu.int)
Fiber-optic
transmission and networking: the previous 20 and the next 20 years
Scaling
capacity of fiber-optic transmission systems via silicon photonics
Optical Communication Systems
|