6G Wireless
Systems: The Shift to 6G Communications: Vision and Requirements

 

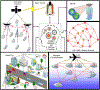

| The
sixth-generation (6G) wireless communication network is expected
to integrate the terrestrial, aerial, and maritime
communications into a robust network which would be more
reliable, fast, and can support a massive number of devices with
ultra-low latency requirements. The researchers around the globe
are proposing cutting edge technologies such as artificial
intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML), quantum
communication/quantum machine learning (QML), blockchain, tera-Hertz
and millimeter waves communication, tactile Internet,
non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA), small cells
communication, fog/edge computing, etc., as the key technologies
in the realization of beyond 5G (B5G) and 6G communications. In
this article, we provide a detailed overview of the 6G network
dimensions with air interface and associated potential
technologies. More specifically, we highlight the use cases and
applications of the proposed 6G networks in various dimensions.
Furthermore, we also discuss the key performance indicators (KPI)
for the B5G/6G network, challenges, and future research
opportunities in this domain.
Next-generation
communication systems aim to achieve high spectral and energy
efficiency, low latency, and massive connectivity because of
extensive growth in the number of Internet-of-Things (IoT)
devices. These IoT devices will realize advanced services such
as smart traffic, environment monitoring, and control, virtual
reality (VR)/virtual navigation, telemedicine, digital sensing,
high definition (HD), and full HD video transmission in
connected drones and robots. IoT devices are predicted to reach
25 billion by the year 2025, and therefore, it is very
challenging for the existing multiple access techniques to
accommodate such a massive number of devices. Even fifth
generation (5G) communication systems, which are being rolled
out in the world at the moment, cannot support such a high
number of IoT devices. Third generation partnership project
(3GPP) is already working on the development of 5G standard and
has identified massive machine type communication (mMTC),
ultra-reliable and low latency communication (URLLC), and
enhanced mobile broad band (eMBB) as three main use cases for 5G
in its Release 13 (R13).
At the same time,
algorithms for the next generation communication systems, which
will have the performance higher than that of existing 5G
networks, are being developed. A typical 5G communication system
has the capability to support at most 50,000 IoTs and/or
narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) devices per cell. Specifically, a more
robust network must be designed to realize the massive access in
beyond 5G (B5G)/6G communication systems.
Currently, there
is little information about the standards of 6G. However, it is
estimated that the international standardization bodies will
sort out the standards for 6G by the year 2030. The work at some
of the research centers has shown that 6G will be capable of
transmitting a signal at a human computational capability by the
year 2035. While the rollout of 5G is still underway, the
researchers across the world have started working to bring a new
generation of wireless networks. A tentative timeline for the
implementation of 5G, B5G, and 6G standards by international
standardisation bodies is shown in
Fig. 1 with respect to the vision of 6G wireless networks.
International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication sector
(ITU-R) issued the requirements of International Mobile
Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020 Standard) in 2015 for the 5G
network standards. At the same time, 3GPP issued R13 for 5G
standards. It is predicted that ITU will complete the
standardization of 6G (ITU-R IMT-2030) by the end of the year
2030, whereas 3GPP will finalize its standardization of 6G in
R23. ITU has established a focus workgroup for exploring the
system technologies for B5G/6G systems in July 2018. The Academy
of Finland has founded, 6Genesis, a flagship program focusing on
6G technologies, in 2018. Similarly, China, the United States of
America, South Korea, Japan, Russia have also started the
research for B5G/6G communication technologies. Read more
at:
|
TACS Science
Technology Engineering and Consulting Delivers The Insight and Vision on Information
Communication and Energy Technologies for Strategic Decisions.
TACS is Pioneer and Innovator of many Communication Signal
Processors, Optical Modems, Optimum or Robust Multi-User or
Single-User MIMO Packet Radio Modems, 1G Modems, 2G Modems, 3G
Modems, 4G Modems, 5G Modems, 6G Modems, Satellite Modems, PSTN
Modems, Cable Modems, PLC Modems, IoT Modems and more..
TACS scientists engineers and consultants conducted fundamental scientific research in
the field of communications and are the pioneer and first
inventors of PLC MODEMS, Optimum or Robust Multi-User or
Single-User MIMO fixed or mobile packet radio structures in the
world.
TACS is a leading concept technology provider and top
science technology engineering and consultancy in the field of Information,
Communication and Energy Technologies (ICET). The heart of our
Consulting spectrum comprises strategic, organizational, and
technology-intensive tasks that arise from the use of new
information and telecommunications technologies. TACS Science
Technology Engineering and Consulting
offers Strategic Planning, Information, Communications and
Energy Technology Standards and Architecture Assessment, Systems
Engineering, Planning, and Resource Optimization.
|
TACS Science
Technology Engineering is a leading concept technology provider and
top science
technology engineering and consultancy firm in the field of information communication
and energy technologies (ICET).
The heart of our consulting spectrum comprises strategic,
organizational, and technology-intensive tasks that arise from the use of new
information, communication and energy technologies.
The major emphasis in our work is found in innovative consulting and
implementation solutions which result from the use of modern information,
communication and energy technologies.
TACS Science
Technology Engineering and Consulting
- Delivers the insight and vision
on technology for strategic decisions
- Drives
innovations forward as part of our service offerings to customers
worldwide
- Conceives
integral solutions on the basis of our integrated business and technological
competence in the ICET sector
- Assesses technologies and standards and develops
architectures for fixed or mobile, wired or wireless communications systems
and networks
- Provides
the energy and experience of world-wide leading innovators and experts in their fields for local,
national or large-scale international projects.
|









